Understanding Comma-Separated Values (CSV) in Excel
Basics of CSV Format
Comma-Separated Values, commonly known as CSV, is a widely-used data storage format that stores tabular data in plain text form. Each line of the file is a data record, and each record consists of one or more fields, separated by commas. This format is highly versatile and can be used in various applications including Excel, where users can easily import and export data. The simplicity of the CSV format allows for easy data manipulation, and it is an excellent way of organizing large amounts of information in a structured manner.
In Excel, users often encounter the need to separate by comma Excel datasets, especially when they import CSV files. The process involves taking a single column of comma-separated values and splitting each entry into its own cell. This functionality is essential for users who need to analyze and work with data that was originally compiled in a non-tabular format or exported from other software as a CSV file.
Common Challenges with Commas in Text and Formulas
While working with CSV data in Excel, users often face challenges, especially when the text contains commas that are not meant to act as delimiters. For instance, if a field in a CSV is expected to contain a list of items, such as "apples, oranges, bananas," it's essential to ensure these do not get broken up when the data is being separated by Excel. Another challenge arises when a field contains formulas or decimal points, as Excel might misinterpret the intent of the commas.
To overcome these challenges, Excel offers features like 'Text to Columns' that permit a more nuanced approach to data separation. It provides users with the ability to specify custom delimiters and to define the treatment of consecutive delimiters or text qualifiers like quotation marks. This is particularly helpful when you have a mix of actual data separators and commas that are a part of the field content. Careful planning on how to separate by comma Excel data can prevent unnecessary errors during the data manipulation process.
By mastering the use of Excel's data separation functions and understanding the intricacies of the CSV format, users can efficiently organize their data into rows, columns, or individual cells. This sets the stage for sophisticated data analysis, making it possible to harness the full potential of Excel's capabilities in data management and reporting.
Methods for Separating Data
Using Text to Columns for Delimited Data
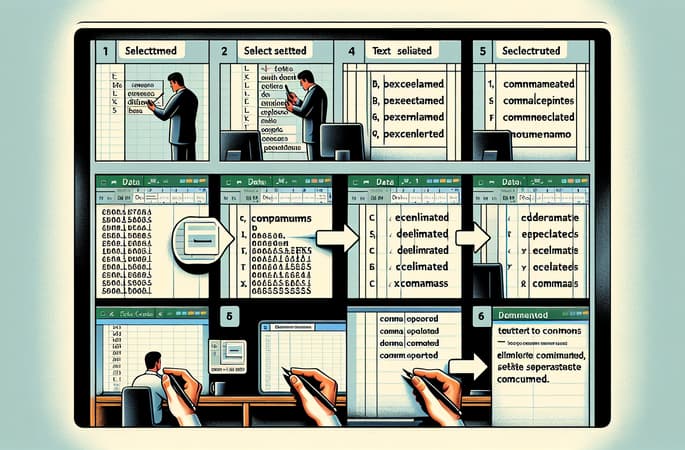
One of the most reliable methods to separate by comma in Excel is by using the 'Text to Columns' feature. This function is incredibly useful when you need to divide data in a single column into multiple, discrete columns. To do this, simply select the column that contains the comma-separated list, and then navigate to the Data tab in Excel's Ribbon. From there, choose 'Text to Columns', and select the 'Delimited' option to split the cell content based on commas or any other specified delimiter.
This feature offers a step-by-step wizard that guides users through the process, allowing them to preview the data as it will appear after the separation. It also provides advanced options to handle different data formats and to skip certain delimiters if necessary. By mastering 'Text to Columns', you can efficiently separate by comma Excel entries and reorganize your data swiftly for better analysis.
Employing Flash Fill to Split Data
Another innovative feature in Excel that can facilitate data separation is 'Flash Fill'. Introduced in more recent versions of Excel, 'Flash Fill' uses pattern recognition to automatically separate data without the need for complex formulas. When Excel detects a pattern in your actions, it will offer to complete the remaining data entries for you. This tool is especially useful when the data to be separated is not consistently delimited or when it follows a recognizable pattern.
To use 'Flash Fill', begin by manually inputting the split data from the first cell into adjacent cells. Once Excel recognizes the pattern, simply press the 'Flash Fill' button in the Data tab or use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+E, and watch as Excel fills in the data for you. This method spawns productivity, making it an excellent choice for those who separate by comma Excel data regularly.
Advanced Techniques for Handling Special Cases
While 'Text to Columns' and 'Flash Fill' handle many scenarios involving comma-separated data, there are instances that require more advanced techniques. Special cases occur when the separated data needs to be operated upon more complex criteria that are not natively supported by Excel's wizards. In such cases, a combination of Excel formulas, such as FIND, LEFT, MID, and RIGHT functions, might come into play.
These formulas can be particularly useful when you need to preserve text enclosed in quotes amidst commas, or when dealing with nested delimiters. They allow for precise control over data extraction and can be customized to suit a variety of complex data separation needs. Expert users who seek to separate by comma Excel data in a more tailored way can greatly benefit from honing their skills in these advanced techniques.
Ultimately, whether you are a beginner or an advanced Excel user, understanding and applying these methods can significantly improve your productivity and data management capabilities. With these tools at your disposal, organizing and analyzing your data in Excel becomes a far more streamlined and efficient process, enabling you to focus on extracting valuable insights from your data.
Working with Commas Within Text
Adjusting Text to Columns Settings
When dealing with complex data where commas serve as both separators and parts of text content, adjusting the 'Text to Columns' feature settings in Excel is crucial. To separate by comma Excel data correctly, the feature offers options for defining text qualifiers. For instance, quotes can be used as qualifiers to signify that commas within them should not act as separators. When importing or working with CSV files, it is important to set these qualifiers before proceeding with the 'Text to Columns' wizard.
By specifying text qualifiers, Excel users can ensure that only the appropriate commas are recognized as delimiters, leaving the integral text and formulas untouched. This level of control allows for accurate data restructuring without the loss or misplacement of crucial information. Additionally, handling complex datasets with varying delimiters becomes more manageable, thus increasing confidence in the data's integrity post-separation.
Utilizing Formulas to Manage Commas in Sentences
In scenarios where 'Text to Columns' may not be sufficient due to intricacies in the data, using Excel formulas becomes a necessary skill to separate by comma Excel content effectively. Complex formulas can identify and manage commas within sentences, effectively separating data while preserving the original intent of the text. A combination of functions such as SUBSTITUTE, CHAR, and TRIM can be used to replace or remove commas within quotes, or to manipulate text strings for accurate data extraction.
For example, the SUBSTITUTE function can replace commas within quotes with a unique character sequence that wouldn't normally appear in the data set, thus allowing 'Text to Columns' to ignore these commas. Post-separation, the SUBSTITUTE function can be applied again to revert the unique sequence back to a comma. Mastering the use of these advanced formulas empowers Excel users to handle even the most challenging data with confidence and precision.
Excel, with its robust toolkit including 'Text to Columns', 'Flash Fill', and a myriad of formulaic functions, provides users with everything they need to effectively separate by comma Excel data structured with both simplicity and complexity in mind. By learning the depths to which these tools can be customized, users can navigate through their data with ease, transforming intimidating data sets into workable and insightful information.
Transforming Data from Columns to Rows
Pasting Comma-Delimited Lists into Separate Rows
When working with comma-delimited data, one common task is to transpose the vertical orientation of a column into a horizontal row format or vice versa. Excel enables users to achieve this through various methods. For those wondering how to paste a separate by comma Excel list into rows, the process can be streamlined using 'Paste Special' feature. After using the 'Text to Columns' feature to separate the data into different columns, you can copy the range of separated data and then use 'Paste Special' with the 'Transpose' option to convert those separate columns into rows.
This method is particularly effective when organizing data for better visualization or when data needs to be formatted to meet specific layout requirements. Excel's 'Transpose' feature is a powerful ally that saves time and maintains the integrity of your data during the transformation process.
Converting Multi-Column Lists to Single-Column Rows
In some instances, users may need not only to transpose data but also to consolidate it from multiple columns into a single, contiguous column. To manage such tasks without manually copying and pasting cell content, which is time-consuming and error-prone, Excel provides several advanced strategies to automate the process.
One of the approaches is to use a combination of Excel functions such as OFFSET and ROW to dynamically reference and stack the data from multiple columns. Another robust solution could be leveraging Excel's Power Query feature, which offers a 'Unpivot Columns' functionality that can transform a set of columns into a streamlined single column with corresponding pairs of identifiers and values.
Whether reorganizing distribution lists, consolidating survey results, or preparing databases, these techniques for converting multicolored lists to single-column rows are indispensable. They enhance the ability to separate by comma Excel data and then transform it into a format that is ready for analysis or reporting within Excel's versatile environment.